L1 optimization by projected subgradient [python]
Published:
Python implementation of Algorithm L1-Minimization by Projected Subgradient from High-Dimensional Data Analysis with Low-Dimensional Models - John Wright, Yi Ma, Page 63
Problem
\(A\) is a matrix with size \(m \times n\), we want to recovery original sparse signal \(x\) from observation \(y\).
\[\begin{align} \min ||x||_1 \\ s.t. \ Ax=y \end{align}\]It is known as basis pursuit and equal to lasso regression
Algorithm 2.2: L1-Minimization by Projected Subgradient (from the book)
Input: a matrix \(A \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times n}\) and a vector \(y \in \mathbb{R}^m\).
Compute \(\Gamma \leftarrow I - A^(A A^)^{-1} A\), and \(\tilde{x} \leftarrow A^{\dagger} y = A^(A A^)^{-1} y\).
\(x_0 \leftarrow 0\).
\(t \leftarrow 0\).
repeat many times
\(t \leftarrow t + 1\)
\(x_t \leftarrow \tilde{x} + \Gamma \left( x_{t-1} - \frac{1}{t} \operatorname{sign} \left( x_{t-1} \right) \right)\);
end while
code
from IPython.core.getipython import get_ipython # for %matplotlib
get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'widget') # install pip install ipympl
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
m = 100
n = 200
A = np.random.randn(m, n)
# A = np.random.random([m, n])
B = A.T @ np.linalg.inv(A @ A.T)
# make x sparse
sparsities = range(20, 60)
success_rates = []
for sparsity in sparsities:
print('sparsity:', sparsity)
tries = 10
success = 0.0
for _ in range(tries):
x0 = np.random.randn(n)
zero_i = np.random.choice(n, n - sparsity, replace=False)
x0[zero_i] = 0.0
y = A@x0
# initialize
x = np.random.random(n)
for i in range(1, 20000):
# print(i)
dx = np.sign(x)
lr = 1/i
x = x - lr*dx
x = x - B @ (A@x - y)
err = np.linalg.norm(x-x0, 1)
if err < 0.01:
success += 1
print('\r err: ', err, end='')
success = success / tries
print('\n success rate:', success)
success_rates.append(success)
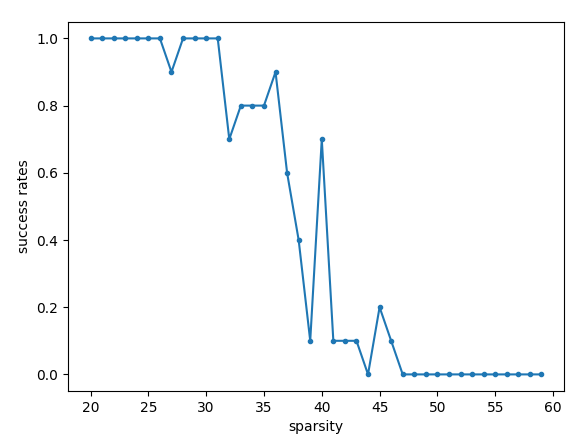
plt.figure(); plt.plot(sparsities, success_rates, '.-'); plt.xlabel('sparsity'); plt.ylabel('success rates')
result